[ad_1]
A penalty from Google is every webmaster’s worst nightmare. But even if you get one, all is not lost.
In this post, you will learn the following:
Thankfully, we have never dealt with penalties on Ahrefs’ blog, so I reached out to SEO experts who deal with Google penalties in their professional work:
Let’s rock!
In simple terms, a penalty is a “punishment” manually imposed on a website by Google’s webspam team.
This generally happens when the website violates Google’s quality guidelines. This penalty results in a dramatic drop in rankings and organic traffic loss. It’s worth mentioning the negative effect of Google’s algorithm updates must not be mistaken for a penalty.
Google does not use the term “penalties” in its documentation. Instead, it calls them manual actions and algorithmic actions.
If your organic rankings and traffic suddenly drop while your website has no downtimes or technical SEO issues, you may be facing one of two things:
- Your website was reviewed by a human and got a manual action.
- A Google update resulted in an algorithmic action demoting your website.
Google’s mission is to present the best results to its users. Its quality guidelines explain what it expects from websites. Any attempt to manipulate its ranking factors or abuse its quality guidelines is called spam.
Every day, Google discovers around 40 billion spammy pages. Here’s how it fights spam.
Google has systems that can detect spam at the “crawling” stage. As a result, a large number of pages considered spammy won’t even make it to Google’s index.
The content included in its index is double-checked for spam. Such low-quality content may be shown in the search results, but its search rankings will be low.
As explained by Google, these AI-aided automated systems provide 99% protection against spam. Manual actions come into play for the remaining 1%.
Google has a vast army of human reviewers who can impose manual actions on websites.
In 2020, they sent 2.9 million messages to site owners in Search Console related to manual webspam actions.
Sidenote.
Manual actions are imposed and lifted by an in-house webspam team in Google. Don’t confuse this team with the quality raters who only help Google with evaluating changes to the algorithms and are not privy to any insights regarding the inner workings of Google Search.
Whenever a website gets a manual action, this issue will always be visible under Security and Manual actions in Google Search Console. It looks something like this.
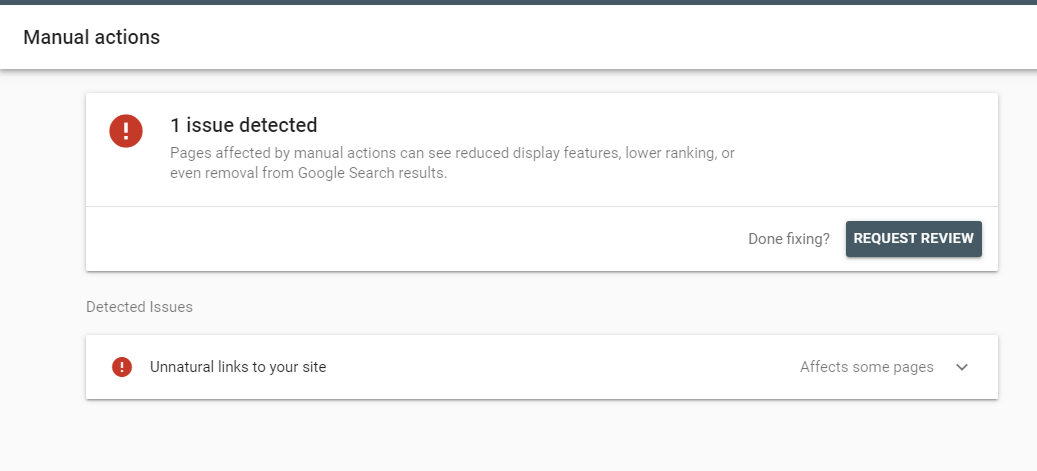
With such a message, you know the problem and can address it directly.
Manual actions imposed on a website will result in pages being ranked lower or omitted from the search results completely.
But diagnosing the effect of an algorithmic adjustment is much more challenging, as you will get zero notifications from Google.
The best way to identify an algorithmic action is to look at your Google organic traffic and see if you have a drop that coincides with a known or suspected algorithm update.
You can search through webmaster forums or Twitter to see if other webmasters are facing similar issues. Google Search Central Help Community, for example, is an excellent place to start.
With Ahrefs, you can check if other websites in your industry are losing their rankings too.
Let’s use our blog as an example:
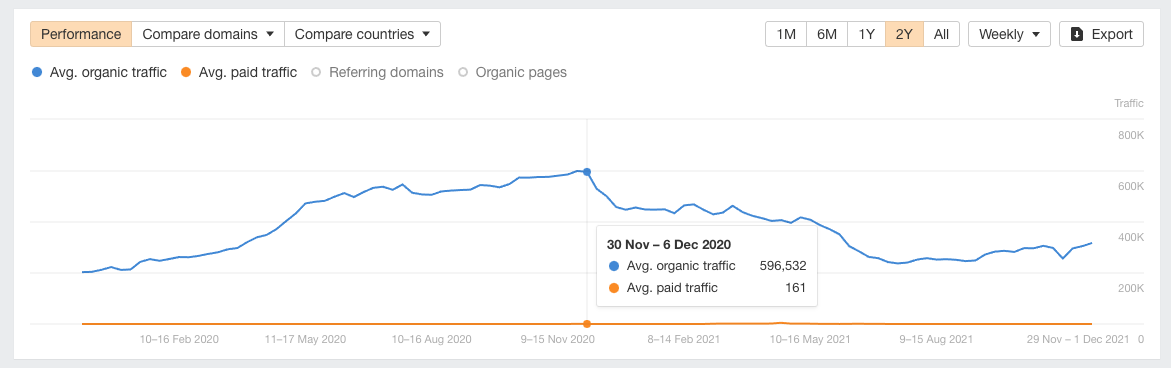
On Dec. 3, 2020, a new core algorithm update was rolled out. Notably, Ahrefs’ blog has the strongest focus on content quality; we have never bought a single backlink. So this update was a slap in the face for us.
You should also note that algorithm updates don’t only demote low-quality or spammy websites; they also promote high-quality sites. So even if there’s nothing “wrong” with your website, you can find other sites outranking you after the next core update.
If you’re ‘hit’ by a core update, you shouldn’t think of it as a penalty. You might not be doing anything wrong at all, it might just be that someone is doing something better.
There are two types of actions that can be displayed on the “Manual actions” page. These are:
- Manual actions that affect the entire site.
- Manual actions that only affect a specific URL or section of a site.
Manual actions can be anything from quite broad to quite specific, and very fluid in between. The goal is always to neutralize the issue, and sometimes that’s easy to isolate & do, other times it’s much harder, so we end up taking broader action.
Every “manual action” notification is accompanied by “Reason” and “Effects” information.
Today, the list of manual actions includes the following:
- Site abused with third-party spam
- User-generated spam
- Spammy free host
- Structured data issue
- Unnatural links to your site
- Unnatural links from your site
- Thin content with little or no added value
- Cloaking and/or sneaky redirects
- Pure spam
- Cloaked images
- Hidden text and/or keyword stuffing
- AMP content mismatch
- Sneaky mobile redirects
- News and Discover policy violations
Whenever Google rolls out a new spam update, it’s basically targeting the same issues.
The core updates address the relevance and quality of content.
Also, you should note that manual actions can cover different Google products. But if you somehow get a manual action related to Google Discover, your regular rankings should not be affected.
News and Discover are entirely separate products.
News includes newsy-content, not just news publishers.
Discover includes content from across the web, not just news content.
Manual actions can happen for either; if issued, they only involve the particular product issued for.
You can read more about the Manual Actions report in this Search Console Help article.
Unfortunately, there’s no data on the share of different penalties from Google, so I searched through recent threads on different webmaster forums and Twitter.
The most common manual actions that webmasters care to resolve these days are related to the attempts to manipulate Google’s search results. This may be a coincidence, but these penalties are even next to each other on the list of manual actions. These are:
- Unnatural links to your site.
- Unnatural links from your site.
- Thin content with little or no added value.
I would say that almost all Google penalties now are given because the site owner was trying too hard to manipulate Google. Five or six years ago I did see a lot of penalties that came as a result of good, honest business owners hiring poor SEO companies who built unnatural links. But, now, most of that type of link is just ignored by Penguin. As such, if you get a link penalty, you usually know that you deserved it.
So stop doing shady stuff, folks! 🙂
Links are still one of the most important ranking factors, so “unnatural links” are the reason behind a large number of penalties these days.
Now, let’s be honest. If you see this notification in Search Console, you most likely participated in a link scheme and know what you’re hit for.
But if you purchased a website or are working on someone else’s website, you’ll need to do a comprehensive link audit. Here are a few quick things that you can work on.
Check your anchor texts
You must pay attention to the dominance of irrelevant or over-optimized anchor texts that come from poor-quality websites.
The first step you should take is to plug your website into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer (or another backlink checker you like) and navigate to the Anchors report. We’ve recently enhanced ours with various helpful filters. Now it’s even easier to diagnose issues related to anchor texts.
With a natural backlink profile, most links are URL-anchored or brand-anchored. But if a site has been heavily involved in manipulative link building, you’ll usually see a lot of keyword-stuffed anchors from multiple referring domains:
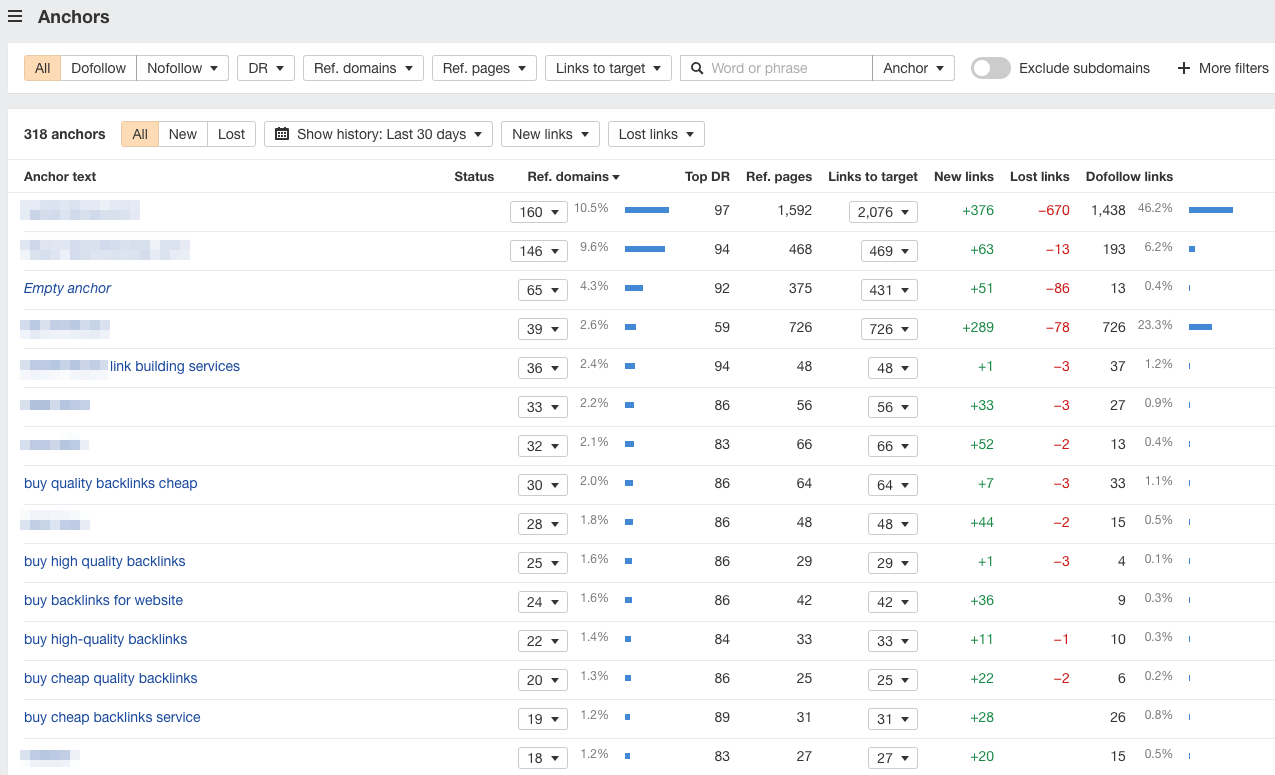
If the Anchors report looks something like this, that’s a bad sign.
As for “Unnatural links from your site,” you should look at the anchor texts of the outgoing links. Ahrefs’ Site Explorer has a special report for that.
Check your referring domains
The Referring domains report in Site Explorer can help you identify websites explicitly built for selling links. The main attribute of such websites is the large number of sites they link to (related to the size of a website).
Besides, these websites usually get little to no traffic from Google, although they may have a pretty high Domain Rating score.
This is why we added “Dofollow linked domains” and “Traffic” columns straight into the Referring domains report.
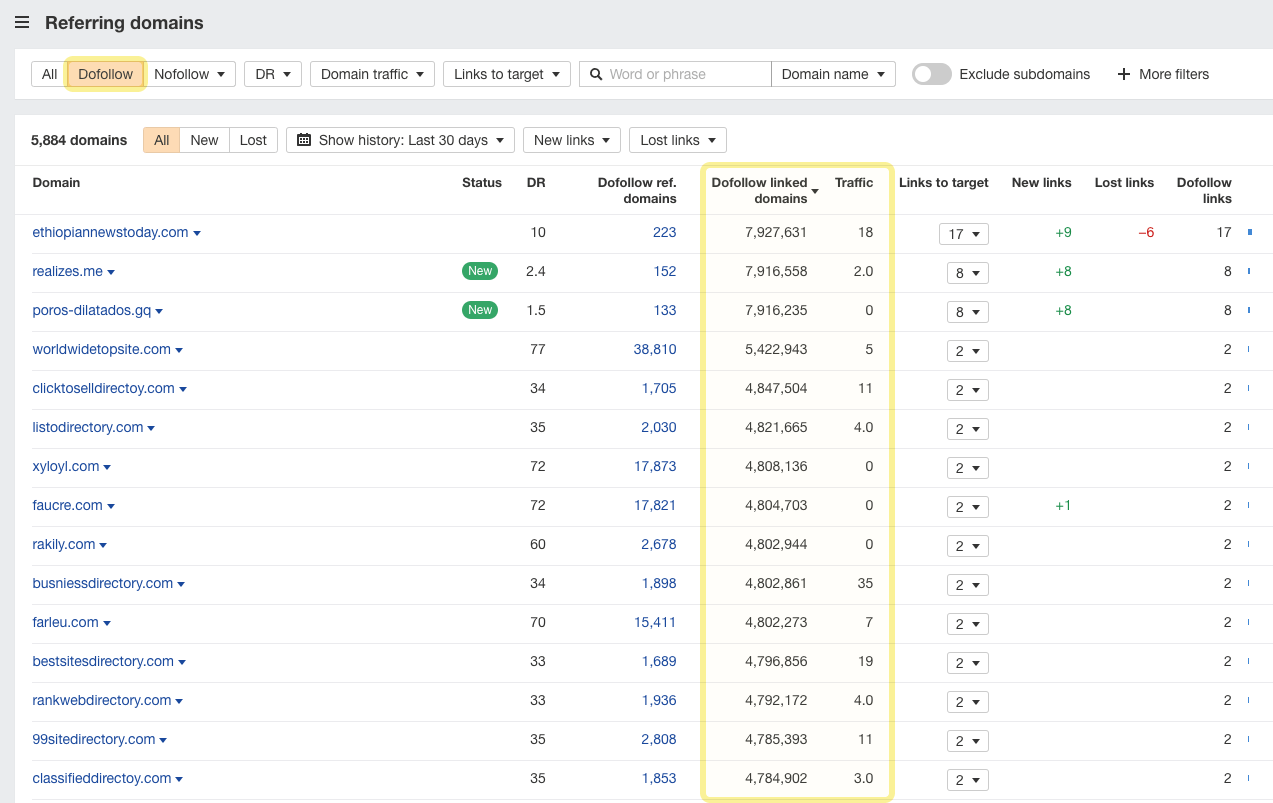
For example, here at Ahrefs’ blog, we’ve never been greedy for external links. If a page or resource deserves a reference, we will link to it.
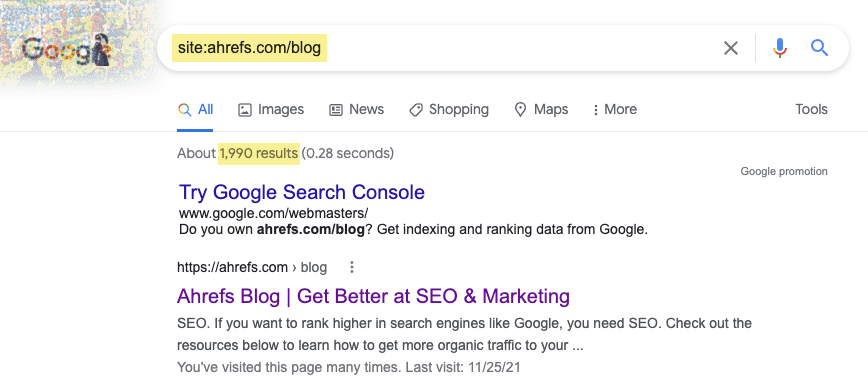
Our blog has approximately 2K pages indexed in Google.
And Ahrefs’ Linked Domains report will show you that we link to around 1.5K websites.
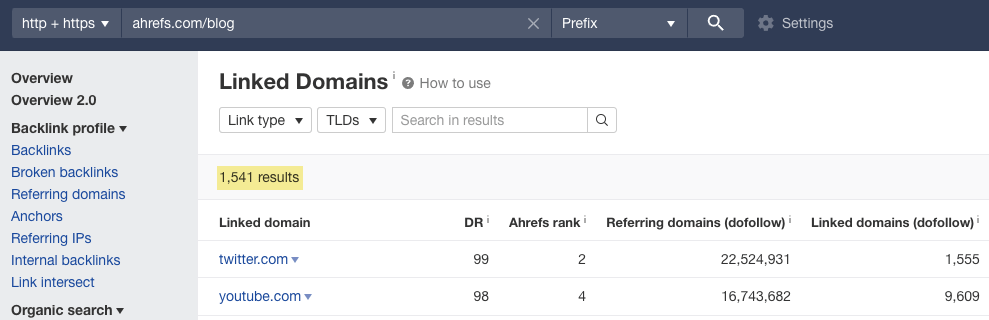
So the ratio is close to 1:1. I’m not saying it’s a standard for every industry, but I hope you get the idea. A website with 500 pages linking to 5K different websites should raise flags.
You should note that a low DR and poor organic traffic do not always indicate a website’s low quality. It could be that the website is new and could grow into a strong one over time.
But when a linking website has low DR, ugly design and UI, low-quality content, and no organic traffic, there’s no way a link from it will be considered natural.
Google seems to have a well-maintained list of websites that sell links. And it may be using link-selling emails to expand that list. Check out this article from Barry Schwartz for more information.
To get a good sense of how serious the link problem is for your site, you can access Marie Haynes’ Disavow Blacklist Bulk Upload tool. Then export the list of your referring domains from Ahrefs and see how many of them are on Marie’s blacklist.
You should also estimate the linking pages visually.
Websites created for the sake of linking out are easily noticeable most of the time. Content on their pages won’t make much sense, and images will be a total mess.
Recommended reading: How to Deal With Unnatural Links & Google Manual Actions
To lift a manual action from your website, you must take actions to rectify the problems specified in the GSC Manual Actions message(s) and select “Request Review” for the particular issue.
“Unnatural links to your site” is the only penalty that has its roots outside your website.
To rehabilitate, you must get rid of those links.
To do that, you need to clean up your link profile as much as possible. Simply disavowing these links may not suffice.
Here’s what Google’s document says:
You should make a good-faith effort to remove backlinks before using the disavow tool. It can also be helpful to document the effort involved in removing those links. Simply disavowing all backlinks without attempting to remove them might lead to rejection of your request.
If you have control over the link, remove it.
Then you should send link removal requests to webmasters. But most likely, this is going to be tough. It will often take you more than one attempt, as you’ll need to look for different contacts before finding the right person.
And even if you reach them, some simply won’t care. And sometimes, they’ll even ask you to pay to remove links.
If you fail to remove a link to your website, disavow the linking page or domain. But do explain why you did so in your reconsideration request.
Make sure to document every step you take and every message you send to fix the issues. This log will make your reconsideration request more convincing.
If the penalty results from thin content, provide evidence of your improvements. Show what content you took down and what you added.
Request a review only when you…
[ad_2]






